

1 冷冻油的循环和分布 | 2 冷冻油与制冷剂的溶解特性 |
3 空调系统性能的测量及计算 | 4 压缩机性能的测量及计算 |
5 与冷冻油相关注意点 | 6 制冷润滑油简介 |
7 润滑油对系统性能的影响 | 8 超低温热泵空调润滑油开发 |
1. 冷冻油的循环和分布
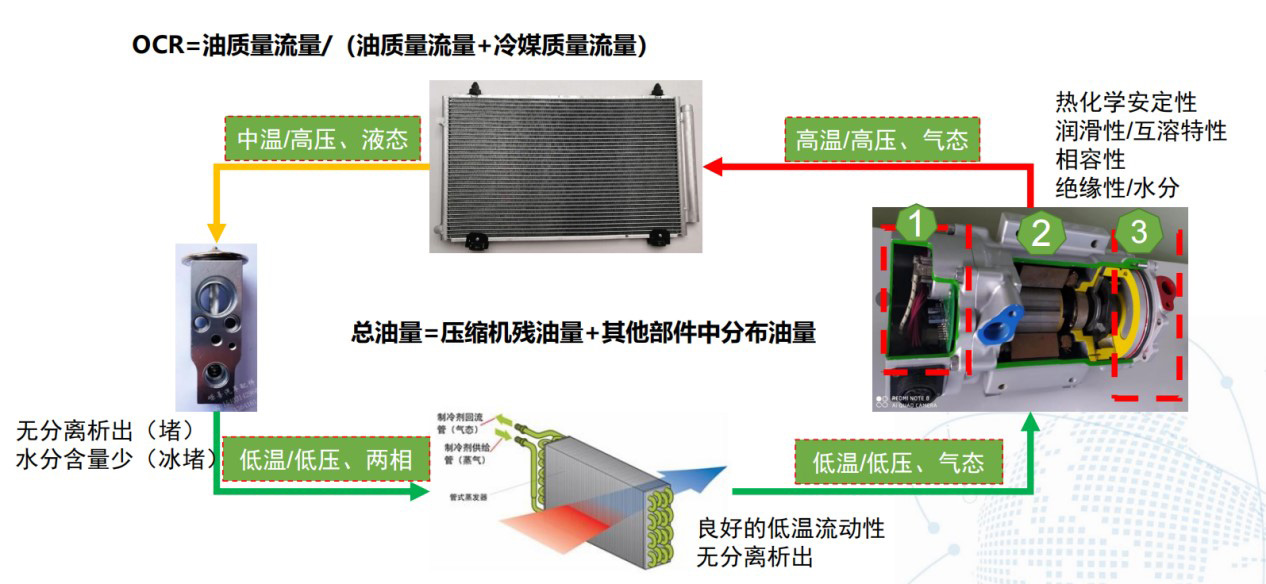
压缩机的残油量与OCR关系

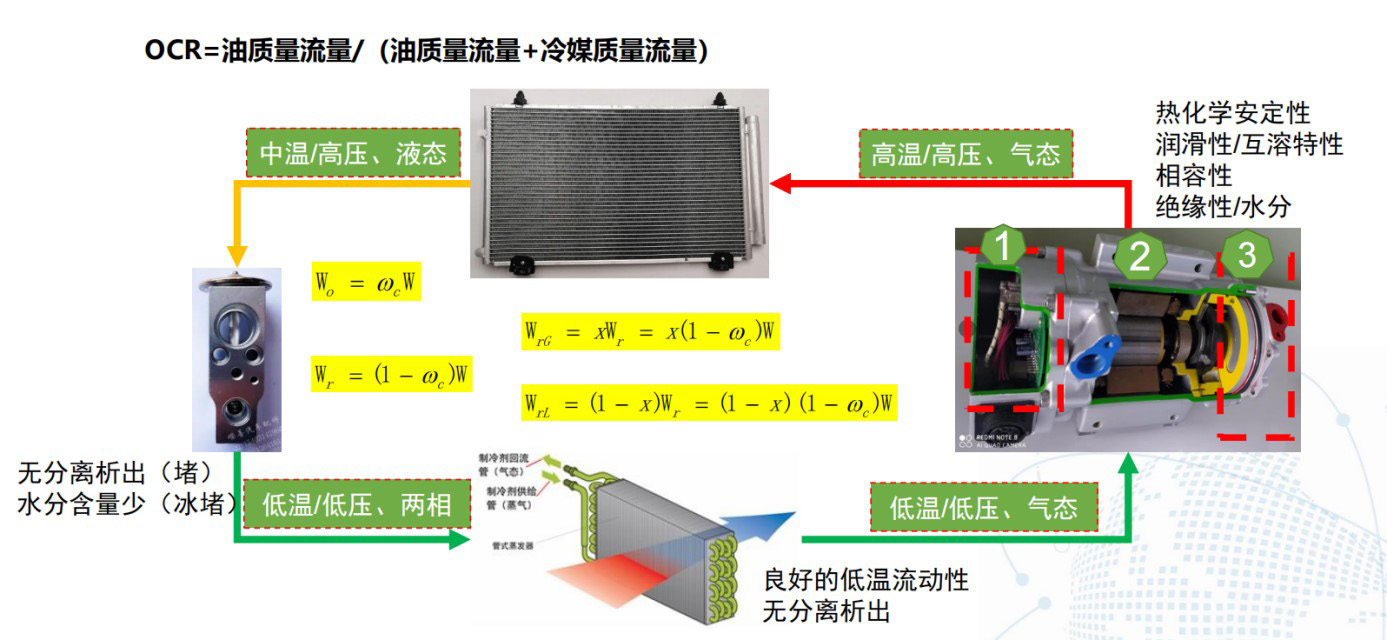
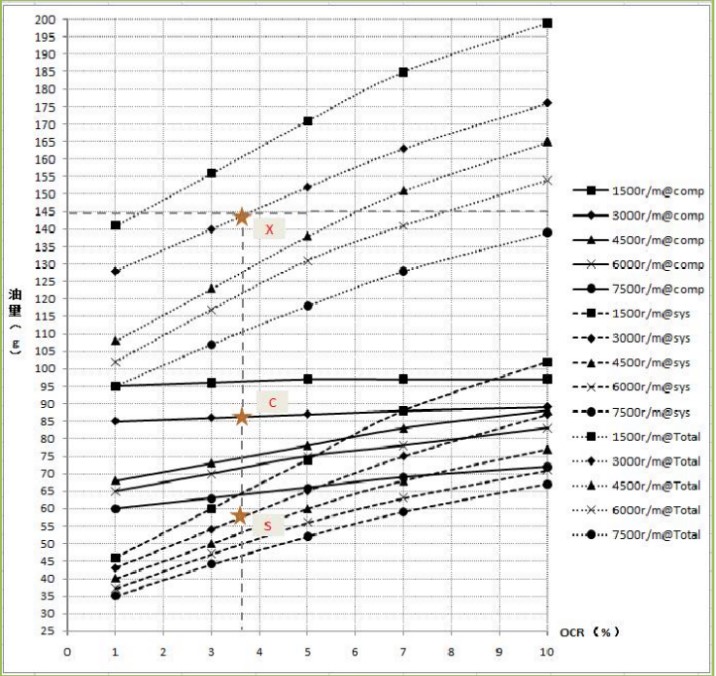
系统油量分布/OCR图解估算方法
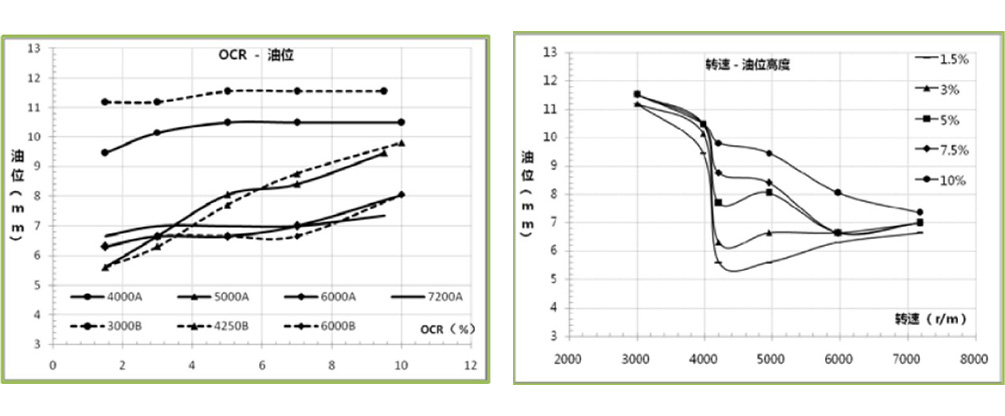
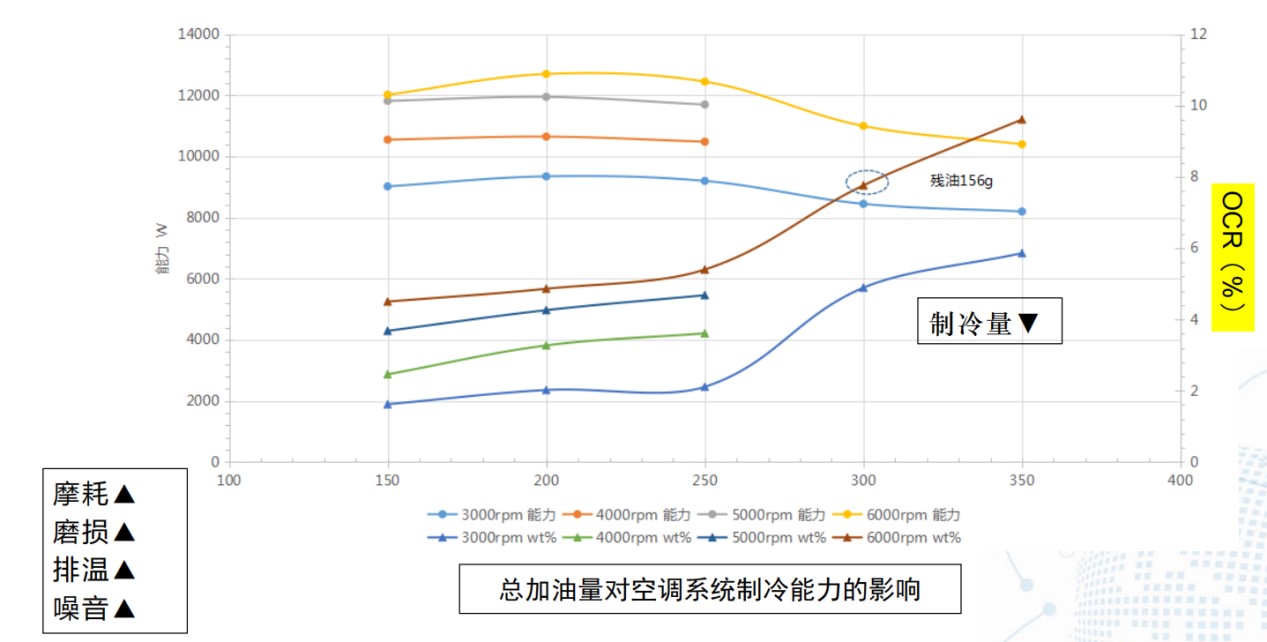
(1)转速越高,OCR越大,压缩机残油量越少;
(2)总油量增加,OCR增大;
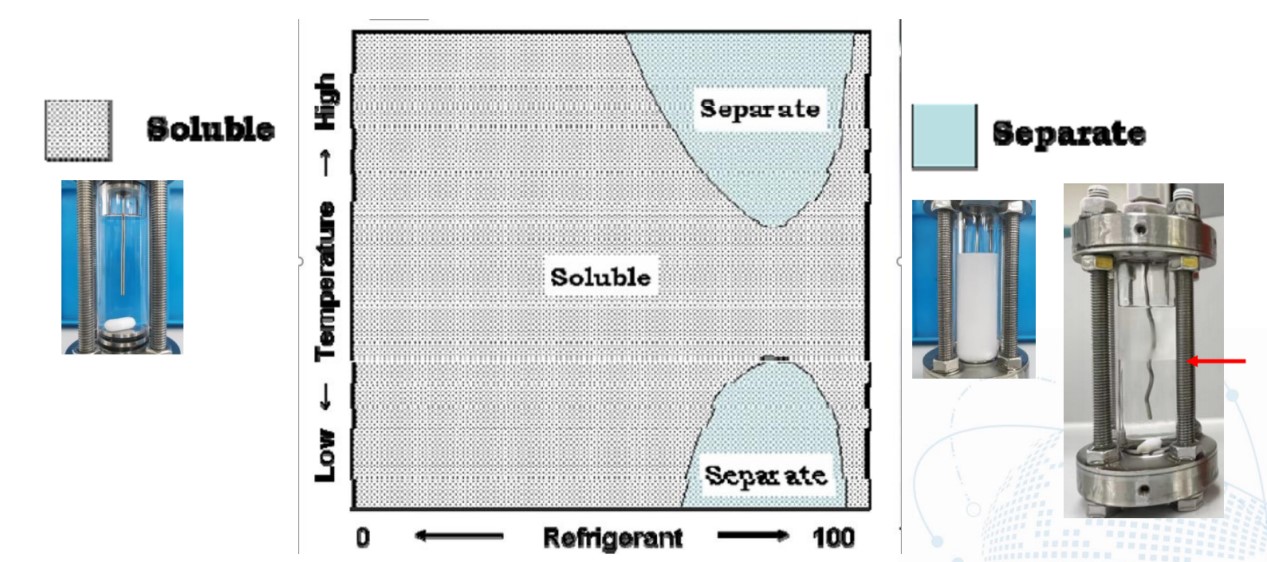
2. 冷冻油与制冷剂的溶解特性
3. 空调器性能测量装置
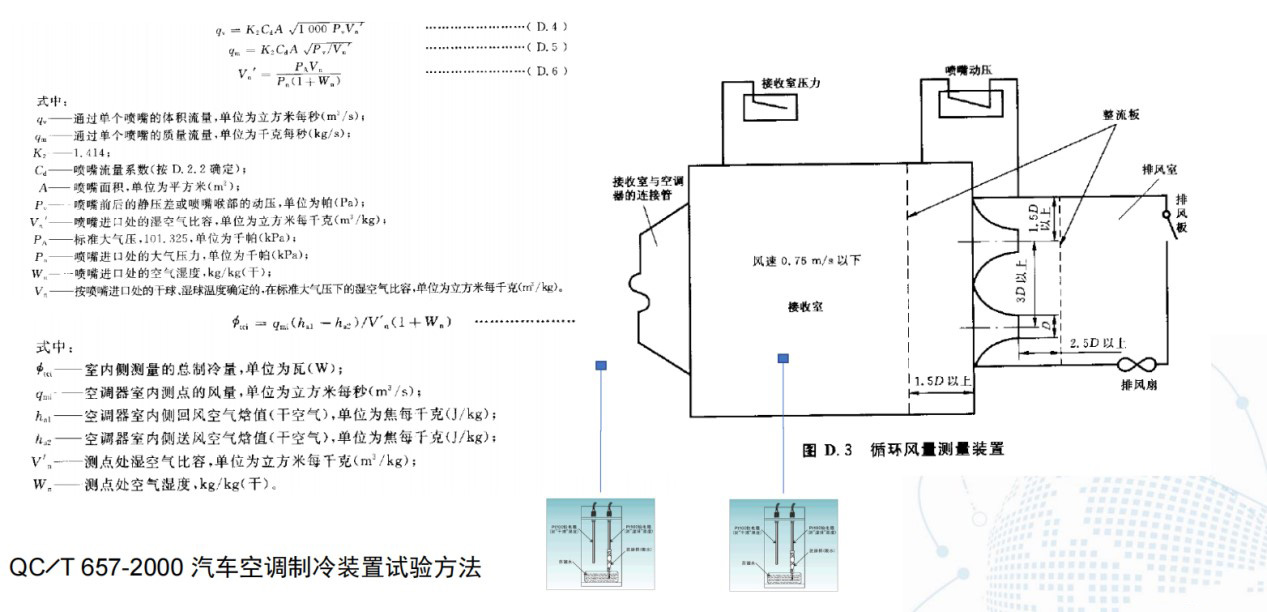
空调器性能计算
冷热水机组性能测量装置

冷冻油对系统性能的影响
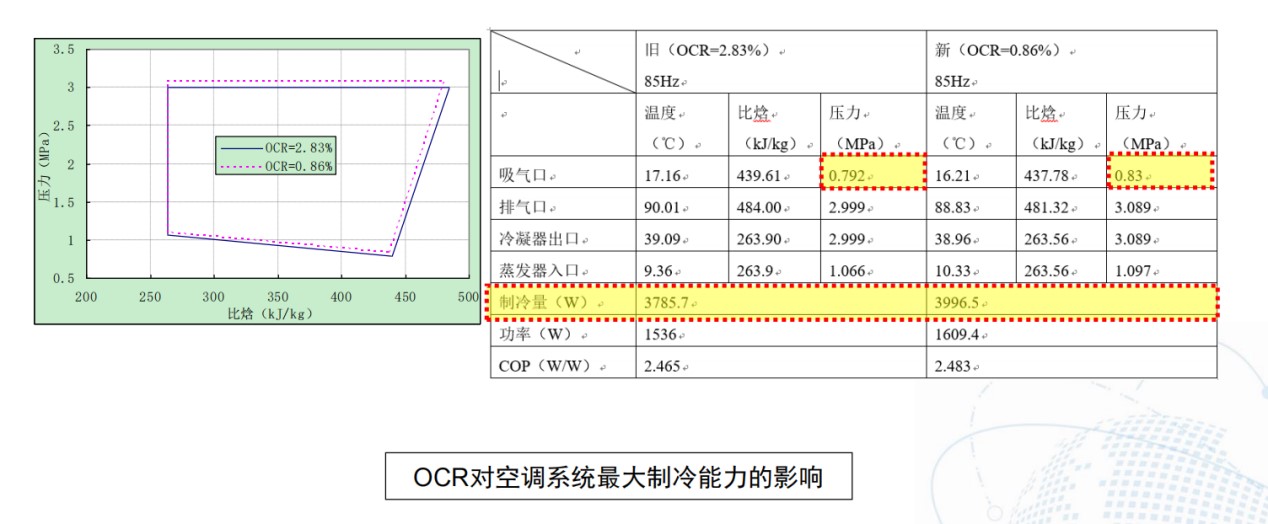
空调系统与压缩机性能差异分析

4. 压缩机性能测试装置
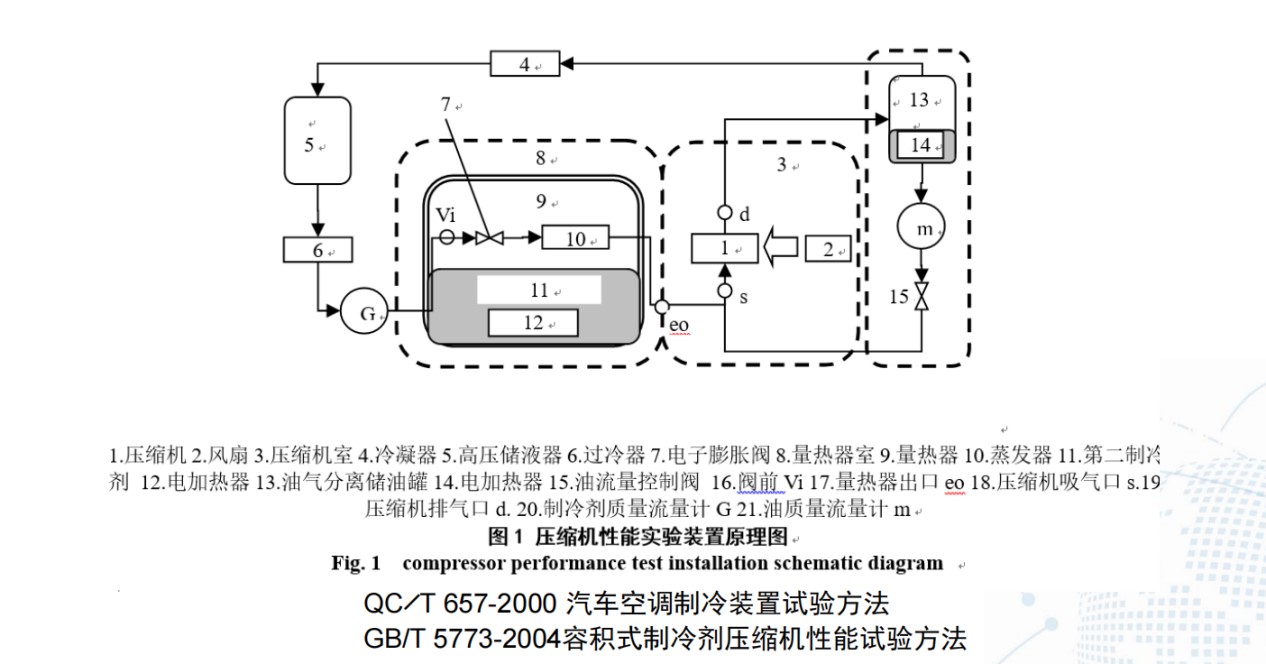
压缩机性能计算

油与制冷剂混合物

油循环对量热器的影响
OCR对压缩机性能的影响
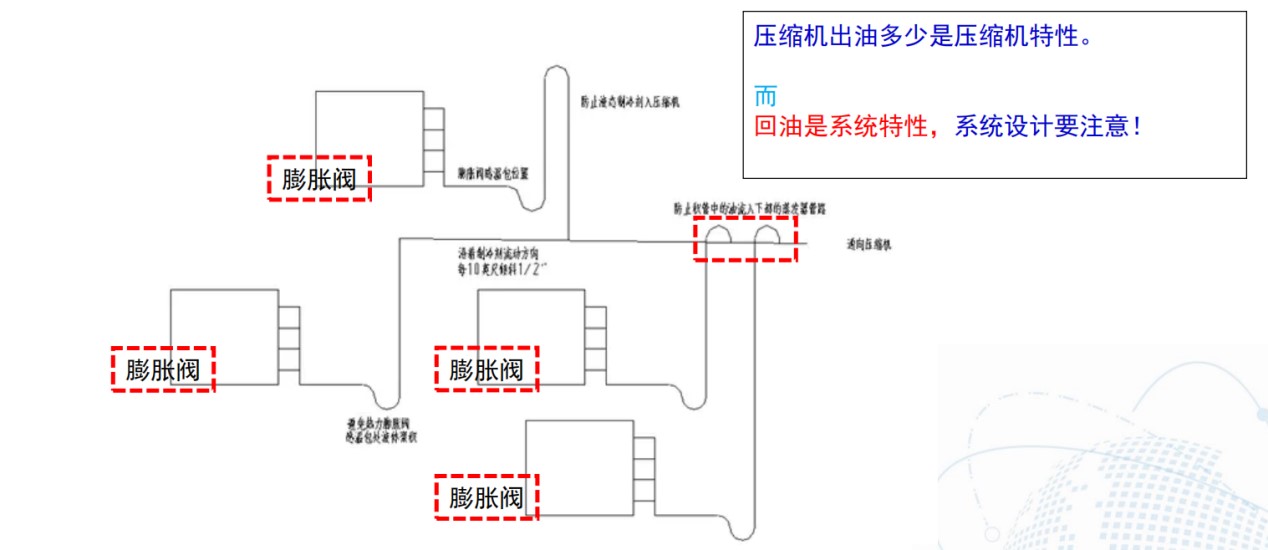
5. 系统回油设计注意点
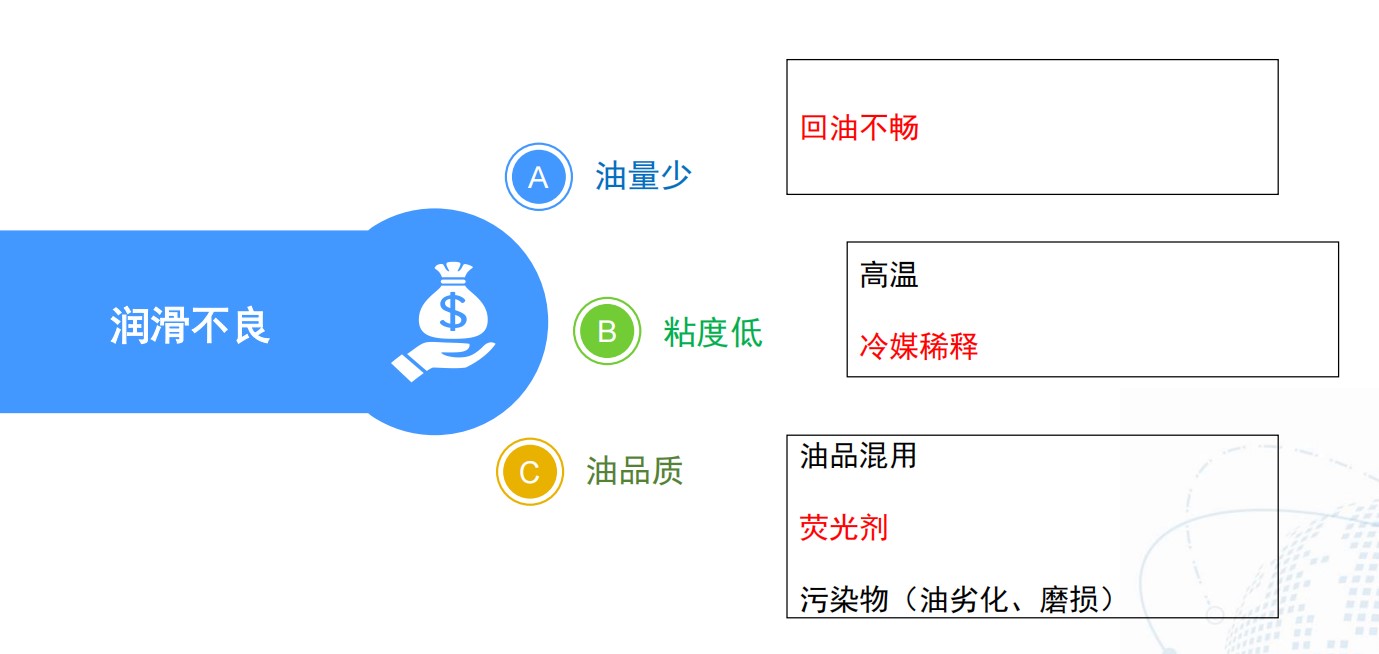
润滑不良
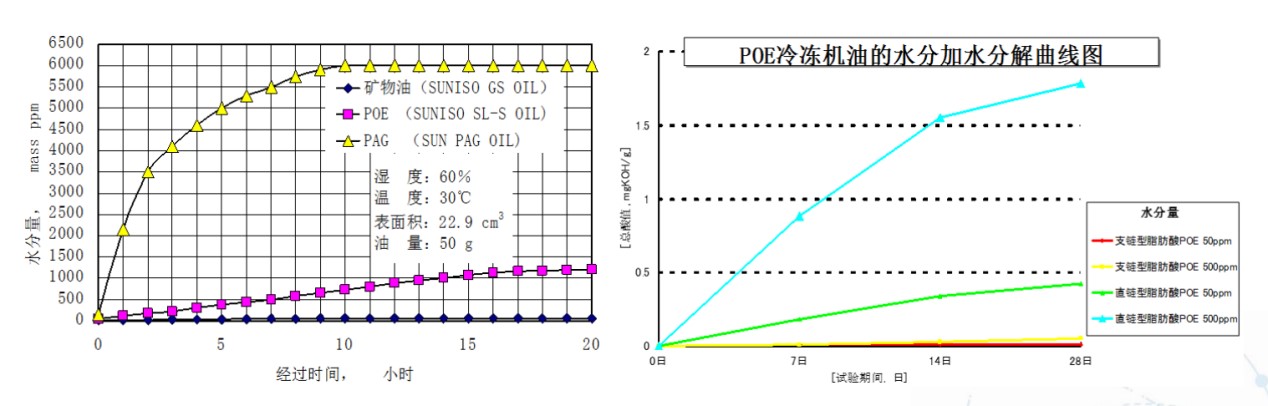
冷冻油的劣化
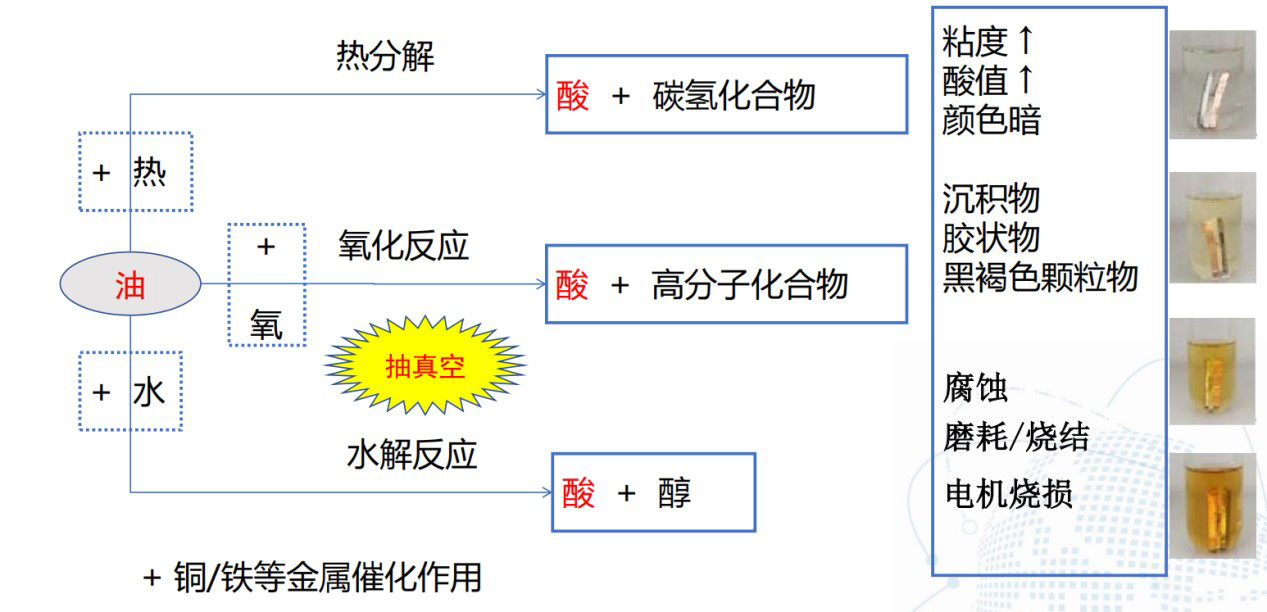
6 制冷润滑油简介
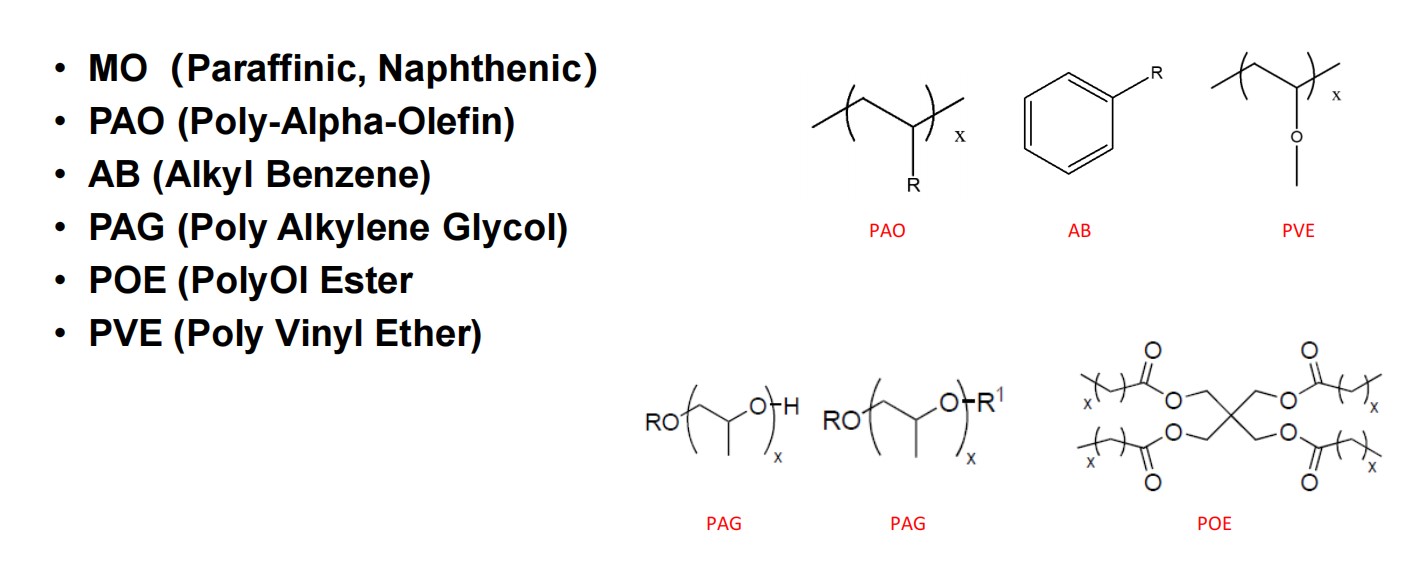
润滑油组成

润滑油组成 - 基础油 Base Oil
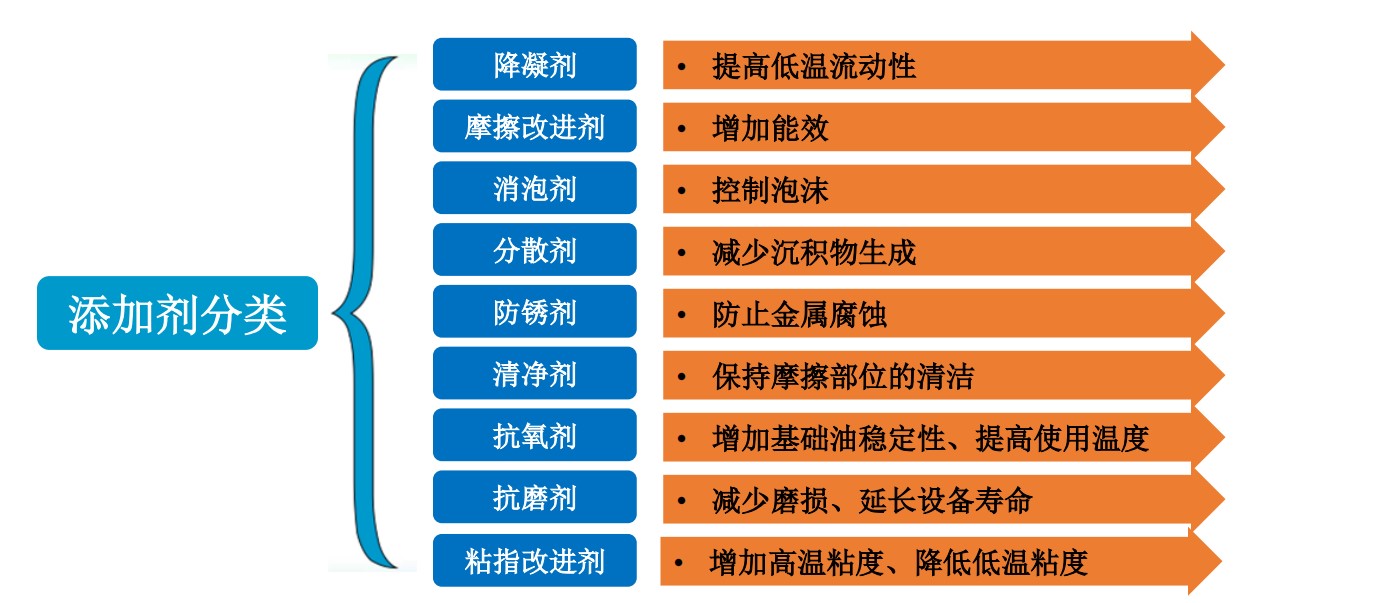
润滑油组成 – 添加剂 Additives
制冷润滑油的特殊性
Why is refrigeration lubricant special?
• 制冷剂不可避免地和润滑油混合,从而影响润滑油的性质
• Refrigerant dissolves in lube and change its properties.
• 全封闭系统:
• Closed system:
• 不换油
• Oil serves for life time
• 受环境影响小
• Less affected by ambient
• 温度、压力变化范围很大
• Significant temperature and pressure change
• 固定工况下,系统有高温高压和低温 低压部分
• high T/P and low T/P in one system
• 不同环境条件下,工况变化大
• Working condition changes with ambient temperature and application
• 不同制冷剂性质不同、应用不一样
• Different refrigerant has different properties and application.
制冷润滑油选择考虑的主要因素
Criteria for Refrigeration Lubricant Selection
• 合适的工作粘度:润滑和回油
• Working Viscosity: lubricity & oil return
• 合适的相溶性:回油和性能
• Miscibility: oil return & efficiency
• 电绝缘性能:安全性
• Dielectric: Safety
• 稳定性:长期可靠性
• Stability: Durability
• 材料兼容性:长期可靠性
• Compatibility: Durability
• 导热性能、比热容等其它性能
• Others: Thermal conductivity, specific heat, et. al
制冷剂和润滑油的主要物性对比
Comparison of physical properties of refrigerants and lubricants
• 饱和蒸气压:差异非常大,>3个数量级
• Vapor Pressure: >3 orders of magnitude
• 粘度:差异非常大,2~4个数量级
• Viscosity: 2~4 orders of magnitude
• 密度:同一数量级
• Density: same order of magnitude
• 导热系数:同一数量级
• Thermal Conductivity: same order
• 比热:同一数量级
• Specific Heat: same order
• 表面张力:润滑油比较大
• Surface tension: Lube is higher

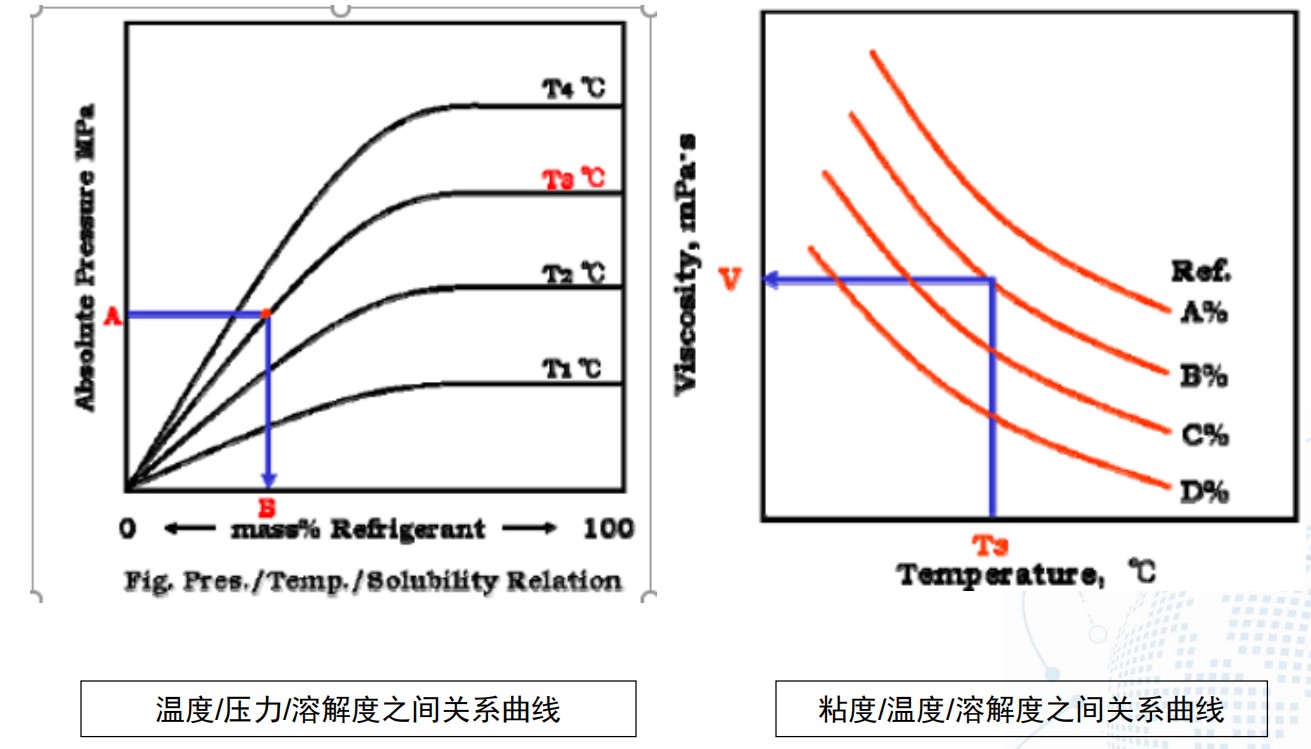
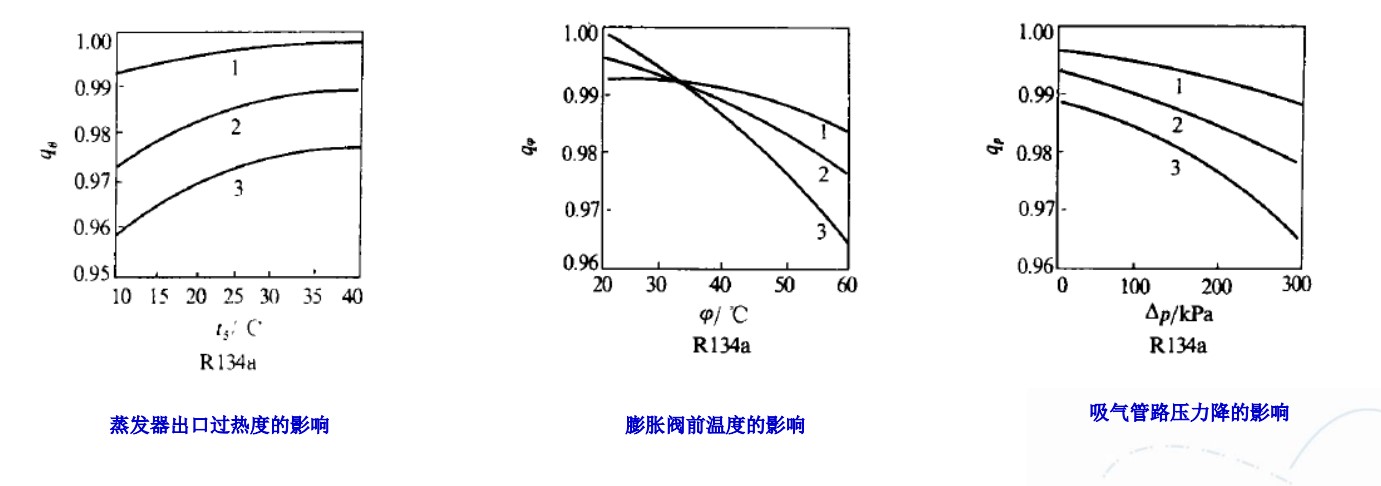
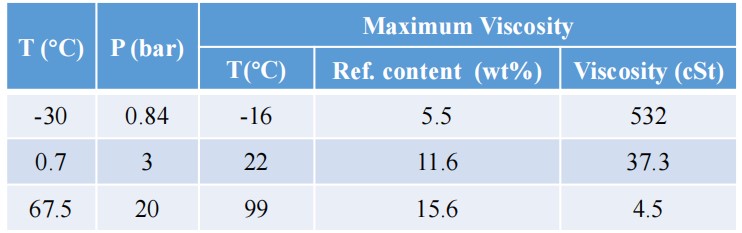
温度、压力对溶解度及粘度的影响
T&P Effect on Solubility and Viscosity
• 制冷剂的溶解会大大降低混合物粘度
Dilution of refrigerant reduces the viscosity of lubricant significantly.
• 恒温条件下,压力升高,制冷剂溶解度增加
At constant temperature, refrigerantsolubility increases as pressure.

温度、压力对溶解度及粘度的影响
T&P Effect on Solubility and Viscosity
• 制冷剂的溶解会大大降低混合物粘度
Dilution of refrigerant reduces the viscosity of lubricant significantly.
• 恒温条件下,压力升高,制冷剂溶解度增加
At constant temperature, refrigerant solubility increases as pressure.
• 恒压条件下,温度升高,制冷剂溶解度降低
At constant pressure, refrigerant solubility decreases as temperature.

温度、压力对溶解度及粘度的影响
T&P Effect on Solubility and Viscosity
• 制冷剂的溶解会大大降低混合物粘度
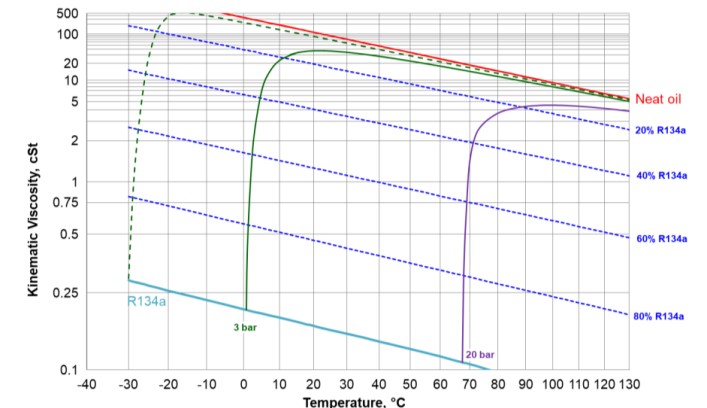
• 恒温条件下,压力升高,制冷剂溶解度增加
• 恒压条件下,温度升高,制冷剂溶解度降低
• 恒压条件下,温度升高,混合物粘度先增加后降低
At constant pressure, as temperature rises, mixture viscosity goes up quickly first and then goes down slowly
7.润滑油对系统性能的影响
Lubricant Effect on Performance of Refrigeration System
润滑油对压缩机的影响
Effect on Compressor
• 润滑:减小磨损
• Lubrication: reduce wearing
• 足够的粘度:温度、压力、制冷剂对油粘度的影响
• Enough viscosity: T, P and Refrigerant affects viscosity
• 供油:结构设计、注油量、系统回油
• Oil supply: Design, Oil charge, Oil return
• 合适的添加剂
•Additives
• 冷却
• Cooling
• 油的传热性能
• Heat transfer
• 油的流动
• Flowability
• 密封
• Sealing:
• 足够的粘度
• Enough viscosity
润滑油对压缩机的影响
Effect on Compressor
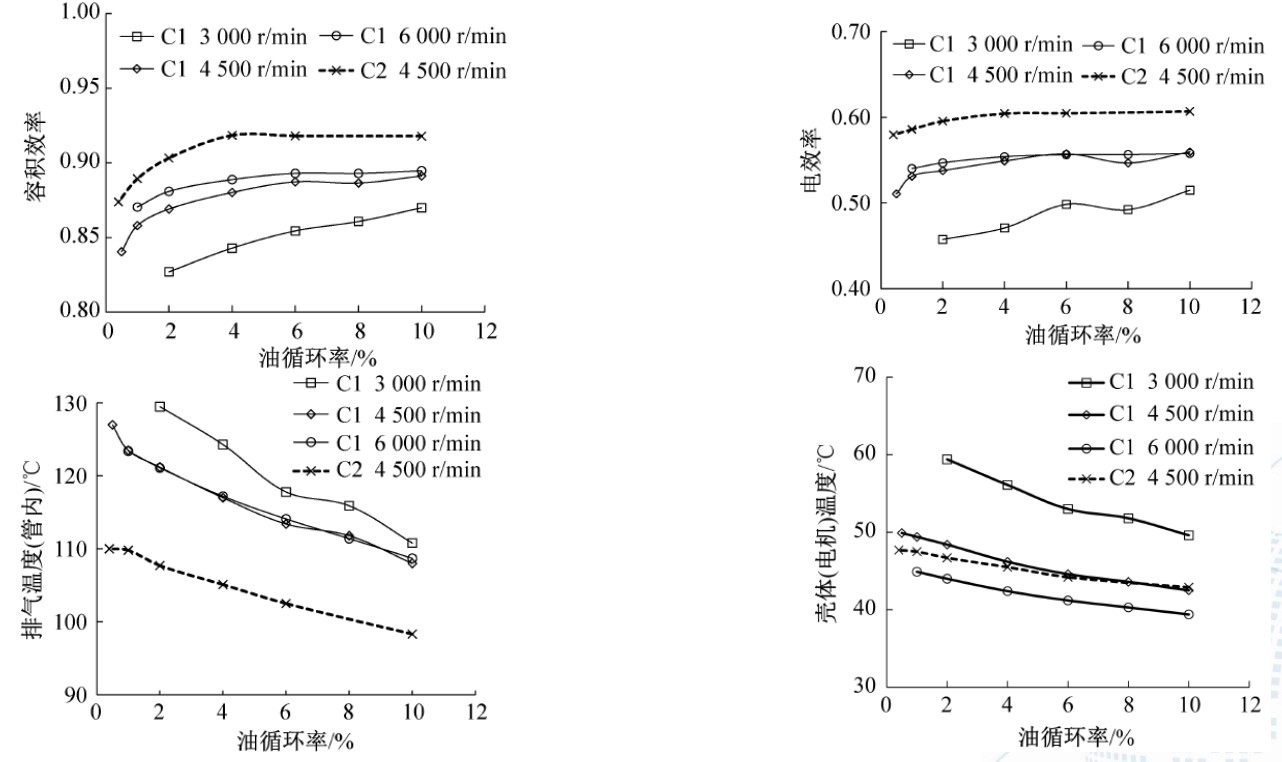
• 正常运转:随OCR增加
• Stable running condition: as OCR increases
• 容积效率先增加后降低:密封变好、 有效吸气容积减少、排气流动阻力增加
• Volumetric efficiency goes up first and then down: Better sealing, effective suction volume reduces, flow resistance on discharge increases
• 制冷量及COP先增加后降低
• Capacity and COP goes up first and then down.
• 排气温度降低
• Discharge temperature goes down.
• 适当的油循环率才能保证压缩机的性能最优
• Appropriate OCR can ensure optimal compressor performance.
润滑油对压缩机的影响
Effect on Compressor
• 启动:
• Start up
• 冷热循环引起制冷剂迁移,可能导致
• Temperature change could cause refrigerant migration and compressor to run out of oil.
• 由于冷媒溶解到油中蒸气压会降低, 温度相同条件下,制冷剂倾向于往油压缩机缺油多的地方转移。
• Refrigerant tends to transfer to the position with high oil content due to the dissolving of refrigerant reduces vapor pressure.
• 润滑油可能被严重稀释,粘度大大降低 -> 润滑不足
• Oil might be diluted significantly and end with wearing issue.
• 液面高,油循环率增加
• Oil expands and OCR increases.
润滑油对换热器传热的影响
Effect on Heat Transferring
• 蒸发器
• 水平管流动沸腾换热:中低干度下,传热系数随OCR增加而增加;高干度下,先增加、后降低。一方面,增加表面张力,增大延展性,增大接触面积,增加发泡点,换热增强;另一方面,由于粘度增加,换热减弱。
• 光滑管:低干度下,核态沸腾为主,加入润滑油削弱了两相流的换热;高干度下,加入润滑油,形成泡沫后更容易形成环状流,从而增强换热;肋片管:对流换热为主,加入润滑油对换热影响不大,且有和光滑管相反的趋势。
• 分体式家用空调中,热阻先减小后增大。
• 换热量减小;换热系数降低
• 冷凝器
• 粘度增加,对对流冷凝有负面效果,但由于露点温度增加,一定程度上起到补偿作用
• 分体式家用空调中热阻增大
对制冷剂分配的影响 - 蒸发器
Effect on Refrigerant Distribution - Evaporator
• 蒸发器入口为气液两相,容易分液不均
The inlet of evaporator is two phases, maldistribution occurs easily.
• 不同结构的换热器,影响不一样
Different design has different oil effect.

润滑油对制冷剂分配的影响 -冷凝器
Effect on Refrigerant Distribution - Condenser
• 总的说来,冷凝侧温度高,油流动性好
Temperature is high, good oil flowability
• 冷凝器进口,基本上全是气体, 有利于均匀分配
Mostly vapor, easier for distribution
• 即便如此,仍有分配不均
Maldistribution still happens

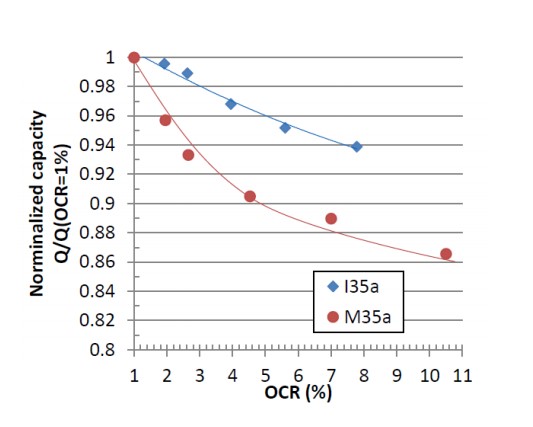
增加OCR对制冷量的影响
Effect of Increasing OCR on Capacity
• 增加OCR,多数情况下冷量降低
Capacity decreases most of the time.
• 低速:OCR从1%增加至8%,制冷量降低6%;高速:OCR从1%增加到10.6%,制冷量减低13.5%。
• OCR从3%降到0.5%,出风温度降低0.8-1.7°C。
• OCR从8-9%降到2-2.6%,制冷量提升8-11%,出风温度降低3-4°C,车内温度降低2-3°C。
• 也有个别报道随OCR增加,制冷量先略微升高后再降低的。
增加OCR对COP的影响
Effect of Increasing OCR on COP
• 增加OCR,COP先增加后减小
COP increases first then decreases.
• 低速:最佳COP对应OCR为2.6%;高速:最佳COP对应OCR为2.0% 。
• 制冷最佳COP对应OCR 为3. 83%;制热最佳COP 对应OCR 为3. 59%。

润滑油对系统可能造成的影响
Possible Lube Effect on System
• 压缩机:可靠性、性能
• Compressor: Durability, Efficiency
• 蒸发/冷凝温度/压力:混合物泡点温度高于纯制冷剂沸点,改变换热温差.
• Evaporation/condensation T/P: Mixture bubble point is higher than pure refrigerant boiling point. Reduce temperature difference at evaporator.
• 换热系数:蒸发器和冷凝器影响不一样,不同研究的结论不统一
• Heat transfer coefficient: Different impact on evaporator and condenser. Inconsistent conclusion in literature.
• 压降:增大换热器、吸排气管路压降->增加功耗、减小质量流量
• Pressure drop: Increase pressure drop across heat exchanger, suction and discharge line. Increase power consumption and decrease mass flow.
润滑油对系统可能造成的影响
Possible Lube Effect on System
• 制冷剂分配:和换热器结构有关,有变 好的情况,也有变差的情况
• Refrigerant distribution: Depending on design, could get better or worse.
• 制冷剂出入蒸发器的比焓差:减小 – 油 不提供制冷量;部分制冷剂溶解在油中不蒸发;油需要被冷却,消耗一部分冷 量
• Reduce specific enthalpy difference in evaporator: Oil does not provide cooling capacity; Dissolved refrigerant could not evaporate; The oil needs to be cooled.
• 制冷剂流量:制冷剂+油的总流量可能增加,但制冷剂流量减小
• Refrigerant mass flow: Total flow of ref and oil could go up, flow rate ref. only goes down.
• 多数情况下,润滑油都对压缩机以外的部分都是带来负面影响
• For most of situations, adding lubricant to the system other than compressor will deteriorate system performance.
8. 电动汽车超低温热泵压缩机润滑油
Lubricant for Electrical Vehicle Super Low Temperature Heat Pump
低温热泵面临的挑战
• 回油:
• 温度更低 -> 润滑油粘度增大
• 温度降低 -> 油/冷媒互溶性变差
• 抗磨:
• 压差增大,摩擦负荷增加
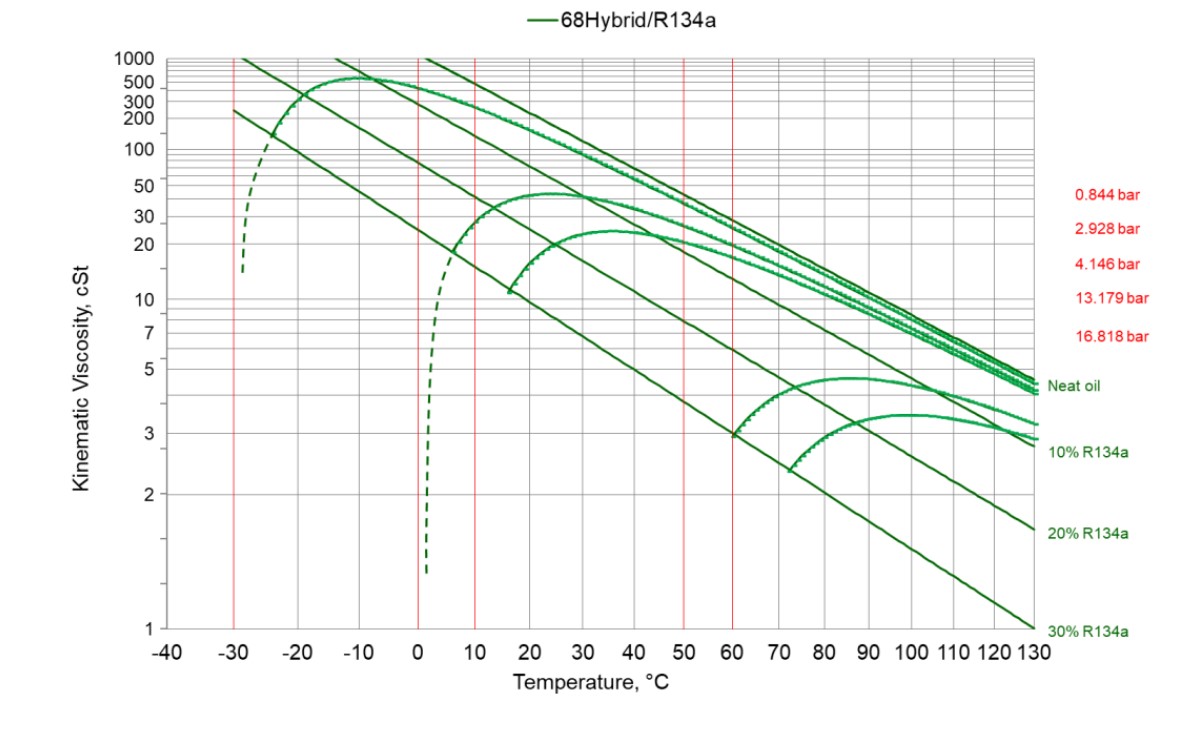
超低温压缩机润滑油
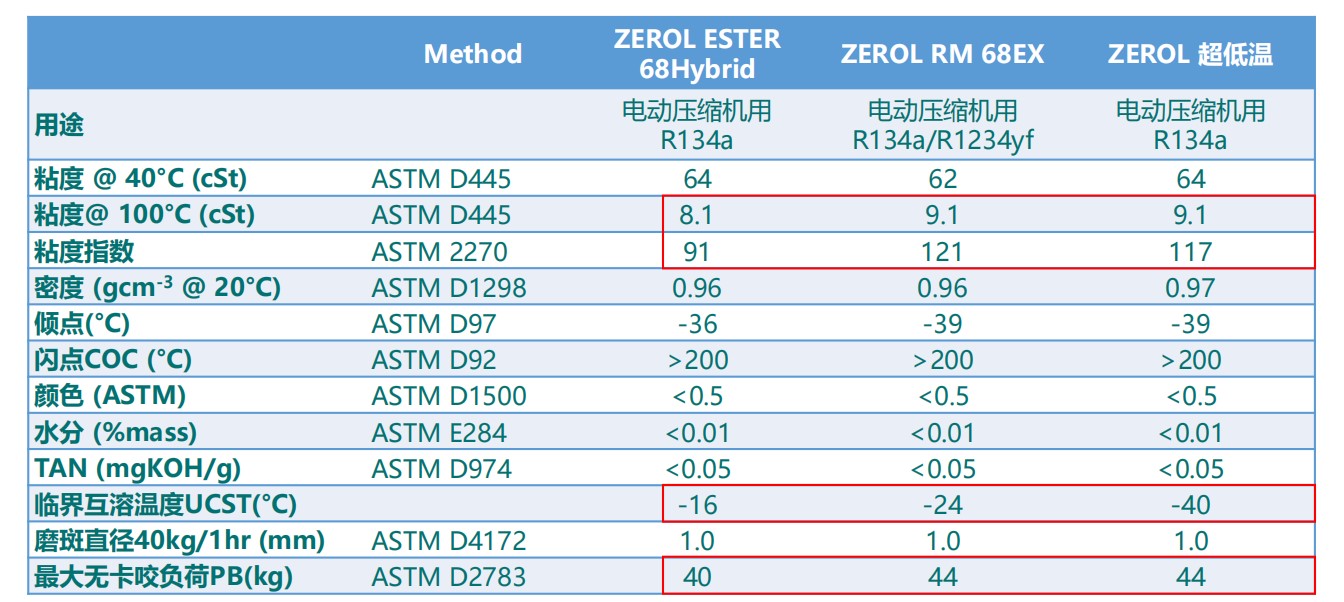
超低温压缩机润滑油: R134a相溶性
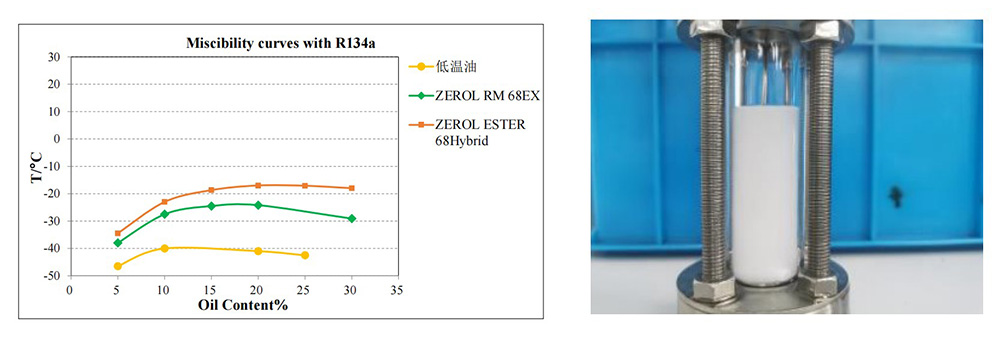
ZEROL ESTER 68Hybrid 在-15℃左右和 R134a即会产生浑浊分层现象,无法适应热泵低温回油的要求

RM 68EX和R134a的互溶性可达-24℃以下
总结 Summary
• 制冷润滑油的选择要充分考虑稳定性、材料兼容性、制冷剂互溶性、及合适的工作粘度。
• Choosing lubricant for refrigeration system should fully consider stability, compatibility, miscibility, and suitable working viscosity.
• 制冷剂和润滑油的物性有很大差别,尤其是粘度和饱和蒸气压,其混合物物性呈现出独有的特点。
• The physical properties of lubricants, especially vapor pressure and viscosity, differentiate from refrigerants significantly. Mixture properties may exhibit unique features.
• 润滑油对压缩机的影响和系统的影响不一样。润滑油的优化可以保证压缩机的可靠性和提升压缩机性能。
• Lubricants have different effects on compressor and the rest of system. Optimization of lubricants can improve compressor efficiency and durability.
• 对压缩机以外的系统中其它部分,润滑油的存在多数情况下是降低系统性能的;个别情况下,润滑油的某些特性,比如起泡、表面张力等,可能起到提升性能的作用。
• For most of situations, adding lubricant to the rest of the system will deteriorate system performance. On some occasions, lubricants may improve system performance due to developing foam, higher surface tension et. al.
加入本菱, 做有挑战的事
Scan the code